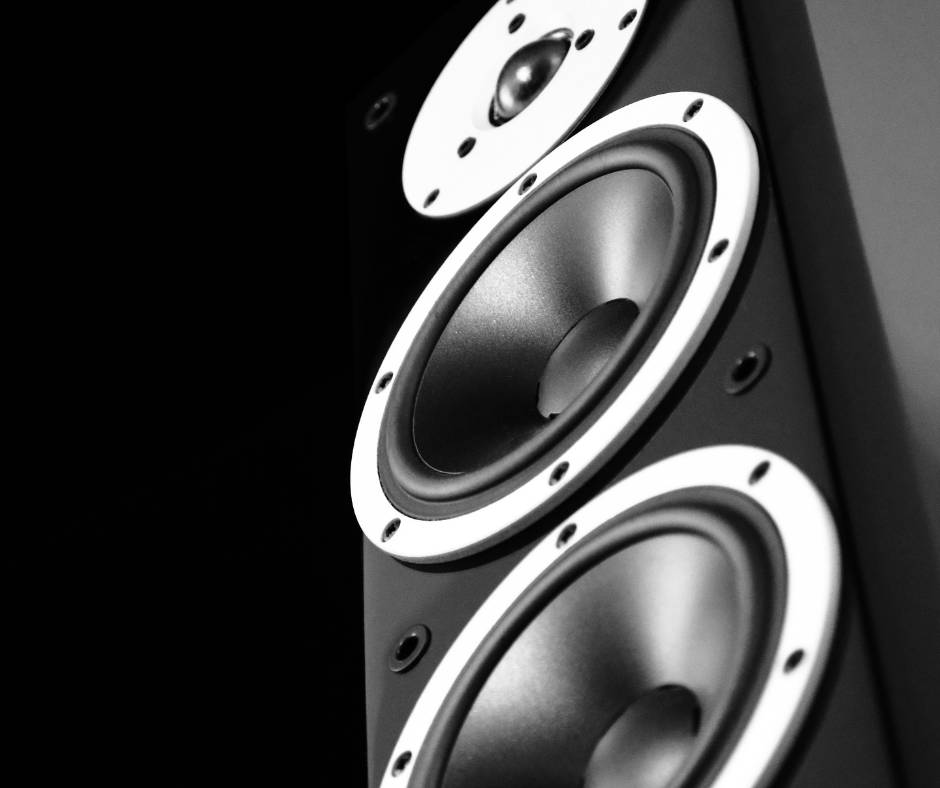
A 2-way tower speaker is a floorstanding loudspeaker that divides sound between a tweeter and a mid-bass driver, while a 3-way tower speaker uses a tweeter, midrange driver and woofer to reproduce distinct frequency bands with greater bandwidth and lower distortion. These configurations—also called two-way systems and three-way loudspeaker architectures—form the structural foundation of floorstanding speaker design and significantly influence clarity, bass extension, dynamic output and overall room performance.
What Defines a 2-Way Tower Speaker?
A 2-way tower uses:
- Tweeter — handles treble and upper harmonics
- Mid-bass driver — handles midrange and low frequencies
This simpler architecture keeps costs lower and ensures excellent coherence. Many acclaimed floorstanding speakers use 2-way designs because of their predictable behaviour, minimal phase complexity and strong imaging performance.
Strengths of 2-Way Tower Speakers
- Better driver integration due to a single crossover point
- Cleaner imaging from close driver spacing
- Simpler crossovers with fewer components
- Higher sensitivity in many designs
- Often more cost-effective than 3-way models
Limitations of 2-Way Towers
- Mid-bass driver must reproduce both mids and bass, increasing distortion at high output
- Less bass extension compared to 3-way designs
- Reduced dynamic headroom in large rooms
A well-executed 2-way tower can deliver excellent musicality, but it cannot match the low-end authority of a full 3-way system.
What Defines a 3-Way Tower Speaker?
A 3-way tower assigns specific tasks to three drivers:
- Tweeter — high frequencies
- Midrange driver — vocals, instruments, mid-band detail
- Woofer — bass and sub-bass output
This allows each driver to operate within an optimised range, reducing distortion and improving clarity, especially in the midrange and bass.
Strengths of 3-Way Tower Speakers
- Stronger bass extension from a dedicated woofer
- Cleaner midrange due to reduced cone excursion
- Higher dynamic capability for large rooms
- Lower distortion across all frequencies
- More powerful full-range sound
Limitations of 3-Way Towers
- More complex crossovers requiring precise tuning
- Higher cost due to additional drivers and cabinet volume
- Placement can become more room-dependent
- Potential for phase irregularities if poorly designed
A 3-way floorstanding speaker excels in delivering scale, bandwidth and realism—particularly in medium and large rooms.
How 2-Way and 3-Way Towers Differ in Sound
At a listening level, engineering differences translate into distinctive sonic characteristics.
Imaging and Soundstage
- 2-way towers often create sharper, more focused imaging
- 3-way towers deliver larger soundstage height and depth
Midrange Accuracy
- 2-way: midrange can be coloured by woofer excursion
- 3-way: midrange clarity is typically superior
Bass Response
- 2-way: limited by shared mid-bass responsibilities
- 3-way: deeper, more controlled bass from dedicated woofer
Dynamic Behaviour
- 2-way: excellent at moderate volumes
- 3-way: superior headroom and scale at higher SPL
Crossover Architecture Differences
The crossover determines how cleanly drivers integrate. 2-way systems use one crossover point, while 3-way systems use two.
2-Way Crossover
- Single handover between woofer and tweeter
- Less chance of phase misalignment
- Clean power response
3-Way Crossover
- Handover from woofer → midrange → tweeter
- Requires more components and tighter tolerances
- Allows each driver to operate in its optimal band
High-end tower speakers often use advanced crossover networks with air-core inductors, film capacitors and multi-order slopes for seamless integration.
Room Size and Speaker Configuration
Both 2-way and 3-way towers can perform exceptionally when matched to the correct room.
Best Rooms for 2-Way Towers
- Small to medium rooms
- Listening distances below ~3 metres
- Spaces where tighter imaging is preferred over maximum output
Best Rooms for 3-Way Towers
- Medium to large rooms
- Open-plan areas needing strong bass output
- Systems intended for cinema, live-level dynamics or full-range listening
Which Should You Choose?
Choose a 2-Way Tower Speaker If You Want:
- Precise imaging and tighter coherence
- Simplicity and smoother integration
- Better budget efficiency
- Strong performance in small spaces
Choose a 3-Way Tower Speaker If You Want:
- Deeper bass and fuller-range sound
- Cleaner midrange at all volumes
- Greater dynamic headroom
- A system optimised for larger rooms
For big, room-filling sound, browse our curated Floorstanding Speakers collection.
Final Thoughts
The difference between 2-way and 3-way tower speakers is more than driver count—it reflects the engineering priorities behind clarity, bass authority and overall scale. A 2-way tower delivers coherence, precision and excellent value, while a 3-way tower provides greater bandwidth, reduced distortion and unmatched dynamic capability. The best choice depends on your room size, listening habits and the level of immersion you want from your floorstanding speakers.